Financial Intelligence Unit – India (FIU-IND) was set by the Government of India vide O.M. dated 18th November 2004 as the central national agency responsible for receiving, processing, analyzing and disseminating information relating to suspect financial transactions. FIU-IND is also responsible for coordinating and strengthening efforts of national and international intelligence, investigation and enforcement agencies in pursuing the global efforts against money laundering and financing of terrorism. FIU-IND is an independent body reporting directly to the Economic Intelligence Council (EIC) headed by the Finance Minister.
The main function of FIU-IND is to receive cash/suspicious transaction reports, analyse them and, as appropriate, disseminate valuable financial information to intelligence/enforcement agencies and regulatory authorities . The functions of FIU-IND are:
- Collection of Information: Act as the central reception point for receiving Cash Transaction reports (CTRs),Non-Profit Organisation Transaction Report(NTRs), Cross Border Wire Transfer Reports (CBWTRs), Reports on Purchase or Sale of Immovable Property (IPRs) and Suspicious Transaction Reports (STRs) from various reporting entities.
- Analysis of Information: Analyze received information in order to uncover patterns of transactions suggesting suspicion of money laundering and related crimes.
- Sharing of Information:Share information with national intelligence/law enforcement agencies, national regulatory authorities and foreign Financial Intelligence Units.
- Act as Central Repository:Establish and maintain national data base on the basis of reports received from reporting entities.
- Coordination:Coordinate and strengthen collection and sharing of financial intelligence through an effective national, regional and global network to combat money laundering and related crimes.
- Research and Analysis:Monitor and identify strategic key areas on money laundering trends, typologies and developments.
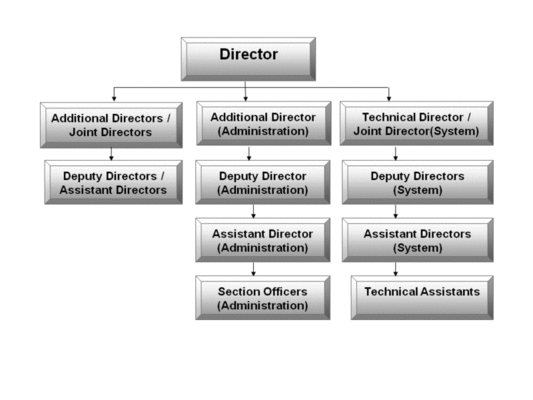
FIU-IND is a multi disciplinary body with a sanctioned strength of 75 personnel. These are being inducted from
different organizations namely Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT), Central Board of Excise and Customs (CBEC),
Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI), Department of Legal Affairs and Intelligence
agencies. The distribution of sanctioned strength is as under:
| S.NO. | POST | Sanctioned Strength |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Director | 1 |
| 2 | Additional Director /Joint Director | 10 |
| 3 | Technical Director | 1 |
| 4 | Joint Director (Systems) (earlier Principal System Analyst) | 1 |
| 5 | Deputy Director (Systems) | 2 |
| 6 | Deputy Director/Assistant Director (earlier Senior Technical Officer) | 21 |
| 7 | Assistant Director (Systems) (earlier System Analyst/ Programmer) | 6 |
| 8 | Section Officer | 2 |
| 9 | Private Secretary | 1 |
| 10 | Personal Assistant | 10 |
| 11 | Technical Assistant | 4 |
| 12 | Assistant | 2 |
| 13 | Data Entry Operator | 3 |
| 14 | Upper Division Clerk | 3 |
| 15 | Lower Division Clerk | 1 |
| 16 | Peon | 4 |
| 17 | Messenger | 2 |
| Total | 75 |
 "
"



